Discover the Perks of Recycling Lives Services for Your Company
Discover the Perks of Recycling Lives Services for Your Company
Blog Article
Checking Out Various Sorts Of Waste in Modern Waste Administration Solution
The contemporary landscape of waste management entails browsing an intricate array of waste kinds, each calling for specialized handling and disposal techniques to reduce ecological impacts. Municipal strong waste, dangerous waste, electronic waste, and organic waste each existing unique difficulties and chances for resource recuperation.
Local Solid Waste
Municipal strong waste, frequently described as house trash or rubbish, incorporates a range of thrown out products produced by property, commercial, and institutional resources within a town. This waste stream generally consists of things such as packaging, food scraps, yard trimmings, paper, plastics, fabrics, and thrown out house products. The management of metropolitan solid waste is an essential element of city planning and public health, demanding effective collection, transport, and disposal systems.
Reliable waste administration systems are designed to lessen ecological effect while making the most of resource healing. This frequently entails a combination of methods including landfilling, recycling, and composting. Recycling programs target materials like paper, glass, metals, and certain plastics, diverting them from land fills and reintroducing them into the production cycle. Composting natural waste, such as food scraps and lawn trimmings, not only decreases garbage dump use but additionally generates beneficial soil changes.
Towns should likewise resolve the logistical and financial obstacles related to waste management. Applying pay-as-you-throw systems, boosting public understanding, and investing in modern technology can considerably boost waste diversion rates. By incorporating these techniques, districts can cultivate lasting areas, decrease greenhouse gas discharges, and save natural sources.
Contaminated Materials

Effective dangerous waste monitoring entails several critical actions: recognition, treatment, segregation, and disposal. Partition makes sure that hazardous materials are kept independently from non-hazardous waste to protect against cross-contamination.
Governing structures, such as the Resource Conservation and Healing Act (RCRA) in the United States, give standards and criteria for hazardous waste management. Adherence to these regulations, paired with advancements in waste treatment technologies, is necessary in alleviating the risks related to contaminated materials.
Electronic Waste
Electronic waste, typically referred to as e-waste, represents a quickly growing obstacle in waste monitoring systems internationally. This kind of waste includes disposed of digital gadgets and equipment such as smart devices, computers, tvs, and various other digital devices. The fast pace of technological improvement, combined with lowering product life-spans and consumer need for the current devices, has actually greatly raised the quantity of e-waste produced each year.
E-waste is especially bothersome due to its intricate structure, often containing unsafe compounds like mercury, cadmium, and lead, which pose significant ecological and health risks otherwise correctly managed. Conversely, e-waste additionally consists of useful materials such as silver, gold, and copper, which can be recouped and recycled. The twin nature of e-waste-- both unsafe and valuable-- requires specific handling, recycling, and disposal processes.
Efficient e-waste management includes rigorous regulative structures, robust collection systems, and progressed recycling modern technologies. Public awareness and engagement are crucial, as improper disposal techniques, such as prohibited unloading and informal recycling, worsen ecological contamination and carcinogen. Subsequently, boosting e-waste monitoring techniques is vital for mitigating ecological impact and recovering beneficial resources in a progressively electronic globe.

Organic Waste
Organic waste, comprising kitchen area scraps, lawn trimmings, and agricultural deposits, stands for a considerable part of the global waste stream. This kind of waste is naturally degradable, meaning it can be damaged down by bacteria into simpler organic compounds. Regardless of its potential for all-natural decomposition, inappropriate administration of natural waste can bring about damaging environmental impacts, consisting of the emission of greenhouse Check This Out gases such as methane, which contribute to climate adjustment.
Effective management of natural waste is critical for reducing these environmental influences (recycling lives services). Composting is a widely adopted technique, transforming organic waste right into nutrient-rich garden compost that can enhance soil wellness and agricultural performance. Furthermore, anaerobic food digestion is an emerging innovation that transforms natural waste right into biogas, a renewable resource resource, and digestate, which can be made use of as fertilizer
Municipalities and waste management entities have to execute durable natural waste collection and therapy programs to maximize the benefits of these procedures. Public education campaigns can also play an essential duty in motivating homes and services to different natural waste from various other kinds of waste. By prioritizing the monitoring of natural waste, cultures can decrease landfill usage, reduced greenhouse gas exhausts, and develop beneficial results for farming usage.
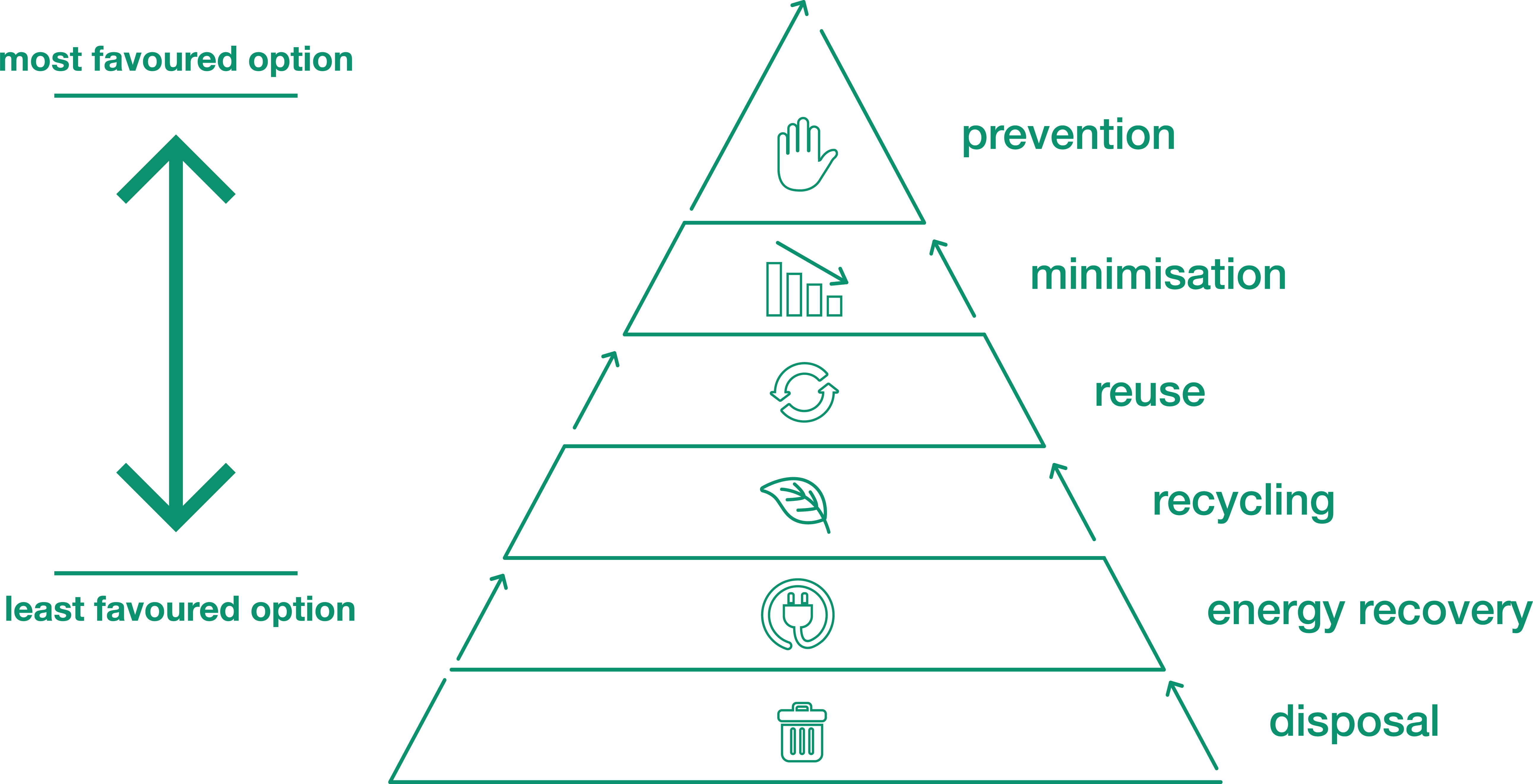
Ingenious Waste Management
In the world of waste management, innovative methods are transforming exactly how cultures manage their refuse, intending for sustainability and performance. These improvements incorporate a variety of technologies and practices that enhance recycling rates, decrease landfill dependence, and reduced environmental influence. One famous innovation is the implementation of clever waste containers equipped with sensing units that monitor fill levels and maximize collection courses. This not just minimizes fuel usage however also minimizes greenhouse gas exhausts.
An additional significant growth is the adoption of helpful hints waste-to-energy (WtE) technologies. By transforming non-recyclable waste into useful power with procedures such as incineration and anaerobic food digestion, WtE reduces land fill problem and offers a renewable resource source. In addition, innovations in chemical recycling permit for the failure of complicated plastics right into their original monomers, making it possible for the development of new, top quality plastic items.
Furthermore, the round economic situation version is acquiring grip, highlighting the layout of products and systems that prioritize reusability and source performance. This alternative approach motivates sectors to minimize waste generation from the beginning. With these ingenious methods, contemporary waste monitoring systems are not only attending to the immediate difficulties of garbage disposal yet also paving the means for an extra lasting future.
Final Thought
An extensive understanding of local solid waste, contaminated materials, digital waste, and natural waste, paired with the implementation of ingenious waste management services, is imperative for reducing environmental effects. Incorporating technologies such as wise waste containers and waste-to-energy systems can improve performance and sustainability. Reliable waste administration approaches not just foster source recuperation yet additionally advertise public awareness and participation, ultimately contributing to the development of a circular economy.
The contemporary landscape of waste administration includes browsing a complicated range of waste kinds, each calling for specialized handling and disposal approaches to minimize ecological influences. Local strong waste, hazardous waste, digital waste, and natural waste each present distinct challenges and opportunities for resource recovery.Digital waste, generally referred to as e-waste, stands for a quickly growing challenge in waste management systems worldwide. Through these cutting-edge methods, contemporary waste administration systems are additional reading not only addressing the prompt difficulties of waste disposal but also paving the method for a more sustainable future.
A comprehensive understanding of metropolitan strong waste, harmful waste, electronic waste, and natural waste, combined with the implementation of innovative waste management remedies, is imperative for minimizing environmental impacts. (recycling lives services)
Report this page